Sample size and pre-screening
Based on effects observed in previous studies2,41,51 with similar experimental designs and factors of interest, as well as counterbalancing requirements, we preregistered and collected 32 valid data sets. An online pre-screening was created to ensure that only non-experts who were familiar with the selection of famous artists would take part in the main EEG experiment. The names of the artists were interspersed with other famous names from different fields (i.e., science, music, and politics). Participants were asked to classify the occupations of the famous people. An alternative option: “I don’t know” was also provided to minimize guessing as a strategy. At the end, participants were asked to indicate whether they had ever studied art or art history (or science, music or politics as distractor questions). Incorrect classification of more than two famous painters and/or confirmation of a formal background in art were exclusion criteria for the main study. Out of the 69 individuals who participated in the pre-screening, 20 people failed the classification task (29%) and none of the remaining 49 individuals had studied art or art history.
Participants
The final sample consisted of 32 (mean age = 26.13; range of 18–37; 18 women) right-handed, native German speakers with normal (or corrected-to-normal) eyesight and normal colour vision. One person had to be excluded and replaced due to a technical error during EEG recording and two due to bad quality EEG data. No participants had to be excluded for incorrectly classifying the valence of artist-related information in the follow-up survey (92.6% correct classification; range 68.8–100%). Participants received monetary compensation or credit points. Before participating, all individuals provided informed consent. The study was approved by the local ethics committee and complied with the standards set by the Declaration of Helsinki.
Materials
The same stimuli and information were used as specified in Experiment 1. The dimensions of the images were adjusted (new total area = 56,400 pixels) to reduce eye-movements during the EEG recording. Viewing distance was set at 70 cm. Visual angles ranged from 4.82° to 7.01° horizontally and from 4.65° to 6.75° vertically, depending on the image pair.
Procedure
The same experimental procedure was used as in Kaube et al.2 (see Fig. 2b). Participants were first required to rate each image for liking on a 5-point scale via button-press. Each trial consisted of a fixation cross, presented for 0.5 s, followed by a painting, which remained onscreen until a participant responded or for a maximum of 2.5 s. The first image presented was consistently a filler, the order of the rest of the paintings was randomised. Participants then rated each image for arousal and quality in the same manner, with the order of the arousal and quality task blocks counterbalanced across participants.
The learning and test phases were constructed in line with previous studies2,41,42,51,52, and conducted separately. During the learning phase, participants were simultaneously presented with an image, the artist’s name and the associated information a total of 4 times. Learning blocks were split into smaller mini-blocks which increased in size to ease the acquisition of knowledge. Again, all participants saw all of the paintings and heard all of the stories, but the assignment of images to conditions was fully counterbalanced across participants. In the first part of the test phase, each post-learning liking trial was repeated a total of 16 times while the EEG was recorded (yielding 256 trials per person or 8192 in total). In the second part, post-learning quality and arousal ratings were measured using the identical trial structure described for the pre-learning ratings. Finally, ratings for the two additional dependent behavioural variables “interest” (“not interesting” to “very interesting”) and “willingness to display” (“definitely would not” to “definitely would”) were obtained in counterbalanced blocks.
After completing the experiment, participants took part in a short follow-up questionnaire to ensure that the presented information had been adequately learnt. They were presented with all of the paintings a final time and instructed to correctly classify whether the information they had learnt about the associated artist was neutral or negative (a pre-defined exclusion criterium required correct classification of more than two thirds of all experimentally relevant images). Participants were also asked to name the artist of each shown image, achieving a correct response rate of 76.6% for images associated with famous artists. All further follow-up measures were identical to those described in Experiment 1.
EEG recording and ERP pre-processing
The EEG was recorded using Ag/AgCl electrodes from 62 scalp sites according to the extended 10/20 system, referenced to the left mastoid. The sampling rate was set to 500 Hz and electrode impedance was kept below 5 kOhm. An external electrode attached below the left eye measured the electrooculogram generated from eye movements and blinks. In a short calibration procedure, prototypical eye movements were obtained to correct for ocular artifacts. Offline, the continuous EEG was re-referenced to a common average reference and band-pass filtered (low cut-off 0.01 Hz, high cut-off 40 Hz). Ocular artifacts were removed by estimating spatiotemporal dipole distributions in BESA57. Further artifacts (defined as segments containing amplitude values ± 200 μV or gradients > 50 μV, or containing baseline drifts) were also excluded from further analyses. The corrected EEG was then segmented into epochs, starting 200 ms prior to stimulus onset and continuing for the duration of the picture presentation. The pre-stimulus baseline was defined as 200 ms prior to picture onset. No electrodes were interpolated and 1.7% of trials were rejected across participants.
A processing pipeline focusing on single trial-based analyses using linear mixed models was implemented to analyse the EEG data58. ERP amplitudes were obtained by averaging across the time-windows of interest at topographical sites typically associated with the components: P1 (electrode sites: O1, O2, Oz, PO7, PO8; 110–160 ms following image onset); N1/N170 (electrode sites: TP9, TP10, P7, P8, PO9, PO10, O1, O2; 150–200 ms following image onset); EPN (electrode sites: PO7, PO8, PO9, PO10, TP9, TP10; 230–330 ms following image onset); LPP (electrode sites: Pz, Cz, C1, C2, CP1, CP2; 400–700 ms following image onset); N400: (electrode sites: C1, Cz, C2, CP1, CPz, CP2 CP2; 300–500 ms following image onset). As anticipated in the preregistration, slight adjustments were made to the preregistered time-frames on the basis of visual inspection of the spatiotemporal profiles of the components (10 ms and 30 ms for the P1 and EPN respectively).
Primary analyses
Our primary analyses focused on the behavioural ratings and the EPN and LPP components. Due to considerations of consistency and comparability, only the first post-learning liking trial was included in the LMM analysing liking ratings. The models analysing liking, arousal and quality were therefore identical to those described in Experiment 1. As there were no pre-learning data for the LMM analyses of the EPN and LPP components and the additional behavioural variables (interest and willingness to display), time of rating was not modelled as an interactive term in these analyses. Random slopes which prevented model convergence were calculated via singular value decomposition and removed.
Secondary analyses
As preregistered, P1, N1/N170 and N400 components were also analysed via LMMs using the same fixed and random effect structures as specified for the EPN and LPP components. We also pooled data for the dimension liking, arousal and quality from both experiments to assess the effects of valence of knowledge and artist renown on these dependent variables with an increased power. As the variables were measured on different scales (7 vs 5), the ratings were z-transformed prior to analyses59. A dummy variable “experiment” with two levels was created, contrast-coded and included in each model as an interactive fixed effect and as an interactive by-item and by-participant random slope. To reduce model complexity, only the after-learning ratings were analysed. Follow-up models, nesting the factor valence of knowledge in the factor artist renown, were also analysed for the ERP components and the pooled behavioural ratings. Results from the follow-up models can be found in Supplementary Material; significant differences are reported below.
Results
Primary analyses
Behavioural ratings
Replicating the results from Experiment 1, after the learning phase, paintings presented in the negative condition were liked less (b = − 0.77, 95% CI [− 0.96 to − 0.58], p < 0.001), found more arousing (b = 0.21, 95% CI [0.02 to 0.41], p = 0.034) and were judged qualitatively worse (b = − 0.39, 95% CI [− 0.58 to − 0.21], p < 0.001), than paintings in the neutral condition. See Fig. 2b. Again, the factor artist renown did not have a significant main effect (liking: b = 0.09, 95% CI [− 0.10 to 0.28], p = 0.331; arousal: b = 0.00, 95% CI [− 0.27 to 0.26], p = 0.979; quality: b = 0.10, 95% CI [− 0.08 to 0.29], p = 0.267) or a modulating effect on these dimensions (liking: b = 0.21, 95% CI [− 0.31 to 0.73], p = 0.423; arousal: b = 0.01, 95% CI [− 0.41 to 0.42], p = 0.969; quality: b = 0.13, 95% CI [− 0.28 to 0.54], p = 0.535). LMMs for the two additional behavioural dependent variables revealed that participants were less willing to display a painting by an artist with a negative biography than a neutral one (b = − 0.65, 95% CI [− 0.86 to − 0.44], p < 0.001) and also rated such paintings as less interesting (b = − 0.22, 95% CI [− 0.42 to − 0.02], p = 0.032). See Supplementary Tables S2 and S3 for full statistical output.
ERPs
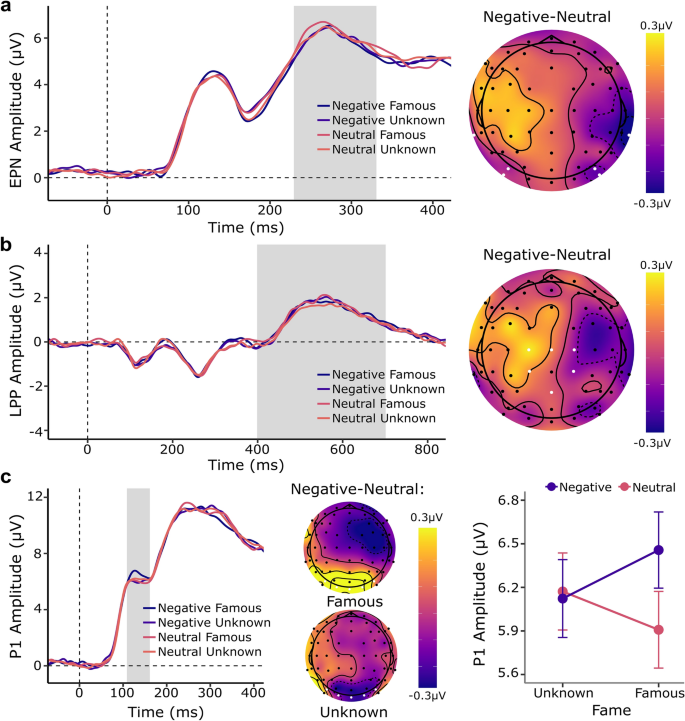
As shown in Fig. 3a, compared to neutral knowledge, negative knowledge about artists elicited an enhanced negativity between 230 and 330 ms in the EPN (b = − 0.27, 95% CI [− 0.49 to − 0.06], p = 0.013). This effect was not modulated by artist renown (b = − 0.17, 95% CI [− 1.07 to 0.74], p = 0.708), nor was a main effect of fame found (b = 0.04, 95% CI [− 0.18 to 0.26], p = 0.712). LPP amplitude was not significantly affected by valence of knowledge (b = 0.02, 95% CI [− 0.28 to 0.32], p = 0.867), artist renown (b = 0.09, 95% CI [− 0.08 to 0.26], p = 0.286), or the interaction between both factors (b = − 0.06, 95% CI [− 0.63 to 0.52], p = 0.838). See Fig. 3b. Full statistical outputs can be found in Supplementary Table S4.
Effect of valence of biographical knowledge and artist renown on EPN, LPP and P1 amplitudes. (a) Grand average event-related potentials and topographical distribution at the region of interest associated with the EPN component. The difference between negative and neutral knowledge resulted in a posterior negativity between 230 and 330 ms (grey area). (b) Grand average event-related potentials and topographical distribution at the region of interest associated with the LPP component. The difference between negative and neutral knowledge did not reach significance between 400 and 700 ms (grey area). (c) Grand average event-related potentials at the region of interest associated with the P1 component. The difference between negative and neutral knowledge resulted in an enhanced P1 amplitude between 110 and 160 ms (grey area). Interaction plot and topographical distributions of negative vs neutral knowledge split by artist renown, reveal that the knowledge effect was driven by information provided about famous artists.
Secondary analyses
Behavioural ratings from pooled data
The effect of negative (vs neutral) knowledge on liking, arousal and quality ratings found in Experiment 1 and 2 was confirmed by the pooled analyse (See Supplementary Table S5). Crucially, there was no interaction between knowledge and experiment (liking: b = − 0.10, 95% CI [− 0.33 to 0.14], p = 0.404; arousal: b = − 0.09, 95% CI [− 0.29 to 0.10], p = 0.345; quality: b = − 0.08, 95% CI [− 0.25 to 0.08], p = 0.319). Despite the increase in power, the effect of knowledge was not modulated by artist renown (liking: b = 0.08, 95% CI [− 0.16 to 0.32], p = 0.528; arousal: b = 0.06, 95% CI [− 0.16 to 0.28], p = 0.577; quality: b = − 0.12, 95% CI [− 0.06 to 0.31], p = 0.183. The main effect of artist renown on quality ratings found in Experiment 1, reached significance (b = 0.10, 95% CI [0.02 to 0.18], p = 0.014), but no effect of artist renown was found for liking (b = 0.05, 95% CI [− 0.05 to 0.15], p = 0.305) or arousal (b = 0.03, 95% CI [− 0.07 to 0.12], p = 0.605). The follow − up nested models (see Supplementary Table S6) revealed numerical differences for the knowledge effect within the artist renown conditions, but the effects remained significant for both famous and unknown artists.
ERPs
Between 110 and 160 ms, analyses revealed a main effect of valence of knowledge on P1 amplitude (b = 0.25, 95% CI [0.03 to 0.47], p = 0.026). This effect was not significantly modulated by the factor artist renown (b = 0.61, 95% CI [− 0.25 to 1.47], p = 0.155), nor was a main effect of artist renown detected (b = 0.03, 95% CI [− 0.30 to 0.37], p = 0.839). Nesting the factor knowledge within the factor artist renown revealed that the knowledge effect was only significant for negative vs neutral information pertaining to famous artists (b = 0.56, 95% CI [0.08 to 1.03], p = 0.024), as opposed to unknown artists (b = − 0.06, 95% CI [− 0.53 to 0.42], p = 0.811). This difference is illustrated in Fig. 3c. See Supplementary Tables S7 and S8 for full statistical output.
No significant effect of knowledge (b = 0.00, 95% CI [− 0.21 to 0.20], p = 0.976), artist renown (b = 0.06, 95% CI [− 0.31 to 0.43], p = 0.729), or an interaction between both factors (b = − 0.38, 95% CI [− 1.24 to 0.48], p = 0.366) could be found on N1 amplitude. For the N400, analyses also did not reveal an effect of knowledge (b = 0.05, 95% CI [− 0.21 to 0.30], p = 0.707). The factor artist renown (b = 0.11, 95% CI [− 0.06 to 0.28], p = 0. 201) and the interaction term (b = 0.06, 95% CI [− 0.46 to 0.57], p = 0.820) did not have a significant effect on amplitude. For full statistical outputs see Supplementary Table S7. Nested models did not reveal significant differences for the factor knowledge when nested in the artist renown conditions separately for N1/N170 or N400 components (see Supplementary Table S8) or for EPN and LPP components (see Supplementary Table S9).
Discussion
In the present study we investigated the influence of social-emotional biographical information about artists on the aesthetic experience of their paintings, whilst taking artist fame into account. We experimentally manipulated the factors valence of biographical knowledge and artist renown in two fully counterbalanced experiments, measuring a range of perceptual, emotional, and evaluative variables via behavioural ratings and electrophysiological markers of brain responses. In Experiment 1, social-emotional knowledge influenced liking, arousal and quality judgments for both famous and unknown artists. This behavioural pattern was fully replicated in the EEG experiment, which further showed that the aesthetic judgments were underpinned by enhanced brain responses associated with low-level perceptual processing (reflected in a modulation of the P1 component between 110 and 160 ms after the presentation of the painting) and early emotional processing (reflected in the EPN component between 230 and 330 ms). The results indicate that affective biographical knowledge about artists not only changes the aesthetic evaluation of an artwork and the emotional arousal associated with viewing it, but it can also penetrate early visual processes underlying the perception of the artwork itself.
In both experiments, paintings by artists who were associated with negative information were liked less and rated as more arousing than paintings by artists presented with neutral information. These findings are fully in line with those of our previous study2, and add evidence to the premise that affective knowledge about an artist can shape emotional responses to a painting. Unexpectedly, and in contrast to the previous study, paintings by “immoral” artists were also evaluated lower in terms of quality. The difference between our earlier and current findings can be explained by the fact that information provided in Kaube et al.2 referred namelessly to the presented painters as “the artist”. The resulting anonymity may have increased the perceived socio-emotional distance between artist and recipient, thereby facilitating a shift to the more detached appraisal necessary when evaluating formal qualities of an artwork “objectively”17. Supporting this perspective, the presence of an artist’s name can exert a top-down influence on various aesthetic judgments60,61 and affects the valuations of paintings in the art market62,63. By providing names, the present study enhanced the credibility of the information, thereby also enhancing the chances to detect effects on outcomes related to authenticity64. We therefore extend our previous findings by showing that knowledge of an artist’s moral transgressions can influence emotional as well as evaluation-based aesthetic outcomes18.
Due to the association between arousal and interest34,35, we expected negative, as opposed to neutral information about artists to increase interest in paintings; however, results indicated a small knowledge effect in the opposite direction (see Experiment 2). While negative stimuli can increase arousal, they can also cause disengagement65, especially when the moral values represented in or by the stimuli are inconsistent with one’s own36. For example, in the artistic realm of fiction, a disparity between the ethical beliefs held by the reader and those propounded by the work can cause the former to (un)intentionally resist further imaginative engagement with the narrative66,67. In the present study, the self-reported decrease in interest may thereby signify an act of rejection intended to demonstrate moral concern68. Negative appraisals of an artwork, in this case elicited by knowledge about its creator, also evoke hostile feelings, such as disgust36,69 which in turn can have behavioural implications; for example, refusing to take a postcard version of the offending picture home36. More generally, individuals are less willing to interact with an object if it was previously owned by someone connotated negatively, due to the well-researched contagion heuristic37,70. In line with this, in the present study, after being exposed to negative biographical information about an artist, participants also demonstrated a significantly reduced desire to display the paintings in their homes.
The influence of affective knowledge on aesthetic outcomes was not modulated by artist renown. Participants were selected on the basis of being highly familiar with the names of the famous artists, while the artists in the unknown condition were entirely fictitious, ensuring participants could not have been familiar with them. Therefore, the absence of a significant interaction between the factors cannot be attributed to a lack of distinction between the artist renown conditions. Instead, our findings suggest that knowing something bad about an artist influences the aesthetic judgments, regardless of whether the artist is well-known or not. A small main effect of artist renown on quality ratings (see Experiment 1) which reached significance in the pooled behavioural data model (see Experiment 2), is in accordance with literature that finds differences in artistic quality of paintings by famous vs non-famous artists20,21. No main effect of artist renown was found for the dimensions of liking or arousal. Participants therefore integrated information about fame into assessments of quality, but made liking and arousal judgments independently. Similarly, in research combining the experimental manipulation of presence of artist name and artist renown, results do not consistently favour the well-known artists60. For example, a famous artist’s work was deemed a better investment than that by a lesser-known artist, but it was not seen as more moving, more aesthetically pleasing or interesting60. Our findings therefore offer further evidence in support of theoretical and empirical accounts denoting the relative independence of different aesthetic outcomes17,18,71,72.
Replicating our original findings, negative knowledge about artists affected early brain responses associated with the automatic processing of emotional stimuli (EPN). The temporal and topographical characteristics of the modulation are comparable to those found in studies investigating the influence of affective information on object and face perception40,42. Our results thus indicate that when individuals are exposed to an artwork by a “bad” person, it can induce a similar emotional involvement as when they are confronted with an image of a “bad” person. Again, we did not find an effect of knowledge on LPP amplitude. Beyond a more controlled and elaborate evaluation of the emotional content of stimuli, the LPP reflects higher-order functions73 which are sensitive to factors such as personal and social significance39,40,74 and task-relevance75,76. Compared to the first study by Kaube et al.2, we increased the personal and social relevance of the information by including names and presenting famous artists that participants were familiar with. The lack of modulation for any of the conditions is therefore likely due to the task. As we aimed to explore processes which occur naturally in an interaction with an artwork, participants were instructed to answer spontaneously and were not explicitly directed to concentrate on the information about the artist when rating the paintings. The LPP is however dependent on attentional processes induced by instructions77,78 and participants may need to consciously attend to the acquired emotional information for affective knowledge based LPP effects to occur78. Moreover, evidence from the field of empirical aesthetics79 indicates that a lateralized late positivity between 500 and 770 ms, reflective of aesthetic appreciation, does not occur spontaneously and requires instruction. In contrast, liking, the rating task during which we recorded the EEG, is readily accessible and does not necessitate intentional contemplation80. To further current understanding of the complex interplay between affective knowledge and task on later processing stages involved in art evaluation, future research should consider recording EEG during multiple tasks and/or varying attention to presented content via differing instructions.
To further elucidate the cognitive dynamics involved in the processing of artworks we also explored the effect of knowledge and fame on ERP components associated with perceptual (P1 and N1/N170) and semantic processing (N400). Analyses revealed that differences between negative and neutral biographical information could be traced as early as 110 ms following stimulus presentation. As the brain activity reflected in the P1 component is linked to the perception of low-level visual features, the finding suggests that we may literally perceive pieces of art, at least in part, in light of our social-emotional knowledge about the artist. The time frame of the modulation aligns with findings from an emergent body of neuroscientific studies that have also observed a significant influence of semantic knowledge on brain activity associated with early perceptual processes47,48,81,82. Such empirical evidence adds credence to the possibility of the penetrability of perception via cognition, a claim subject to much philosophical debate83,84,85. Further planned analyses revealed that the knowledge effect was more pronounced for paintings associated with famous artists, suggesting that basic perceptual aspects of aesthetic experiences may be more strongly affected when we are faced with the work of a renowned artist. Correspondingly, famous faces have been shown to elicit larger P1 responses than unknown faces86, as have negative (i.e., angry) and socially relevant faces74, indicating that the effect may be driven by visual attention.
We did not find effects on N1/N170 amplitude; an electrophysiological marker of higher-level configural processing during perception. As participants in this study were non-experts, this result is consistent with research evincing the component’s functional sensitivity to expertise across multiple modalities and domains87,88,89, including art90. Lastly, the lack of N400 modulation aligns with previous literature which did not find the component amendable to emotional priming91,92. Turning to the time course of aesthetic evaluations as denoted by electrocortical correlates, research indicates that geometric patterns judged as not-beautiful, prompt a frontocentral phasic negativity around 300 to 400 ms93. Our results suggest that negative affective knowledge may be extracted earlier, therefore potentially in time to influence the processes underlying such judgments.
An overarching aim of the present study was to extend the generalisability of previous findings by increasing the external validity of the presented information. Whilst the same images and information were presented in Experiment 1 and 2, there were some methodological differences between the two experiments, including: settings (online vs laboratory), intensity of learning phase (information repeated once vs several times), answer scales (7 vs 5 points), response time (unlimited vs maximum of 2.5 s), structure of learning and test phases (integrated vs separate), screening mechanisms and size of images. Despite these differences, the main behavioural results of Experiment 1 were replicated in Experiment 2, indicating that the found effects are invariant to these additional influences. Further, Experiment 1 was conducted in a physical context more representative of a natural interaction with art viewed in an online environment. Recent developments in technology have rendered online settings a viable way to consume cultural objects, and the increase in virtual galleries and museum exhibitions94,95 confers the ecological validity of investigating aesthetic interactions on screen and in online settings96. Nevertheless, relocating the experimental manipulation to a real-life gallery context would provide invaluable insights into how the physical context and presentation format interact with the reported knowledge effects.
The operationalisation of the artist renown condition required participants to be familiar with the famous artists. The subsequent implemented exclusion and pre-screening mechanisms resulted in a selection of participants who were not experts, but were sufficiently acquainted with the artists to (at least) accurately identify them as painters. This implies a specific level of prior knowledge not generalisable to all people. However, as relativity of prior knowledge is inherently implied by the concept of fame itself (i.e., someone is more or less famous depending on how well and how many people know them), the effect of fame can only be studied with reference to a sample of people familiar with the investigated subject. Examining the influence of artist renown and affective biographical knowledge in a sub-population of formally trained art experts would shed further light on the interaction between these factors and expertise. It should also be noted that, to avoid priming effects, we did not collect a measure of how much participants liked the (famous) artists. As such, the present study does not address the potential modulating effect of prior preference on art perception, nor do we show how acquiring negative information affects feelings about the artists. The role of attitude towards an artist therefore also presents an intriguing line of enquiry for future research.
In conclusion, the presented findings indicate that knowing something bad about an artist affects the aesthetic appreciation of a painting, as well as the perceptual and emotional processes which underlie an aesthetic experience. Affective information about artists, particularly famous ones, elicited an enhanced brain response indicative of the visual encoding of low-level visual properties. We therefore show that negative biographical knowledge about artists not only affects consciously expressed aesthetic judgments, but can shape the actual perception of an artwork as well. Paintings by artists associated with negative information were liked less, found more arousing and evaluated as qualitatively worse that paintings by artists with a neutral biography, regardless of whether the artists were famous or unknown. Following the plethora of accusations against prominent artists in recent years, our cultural attitude towards accountability is currently in flux and the previously reigning belief that art transcends the biography of an artist is under close scrutiny97,98. The neurocognitive insights garnered in the present study can further understanding of the topic by contributing an empirical perspective to the debate.